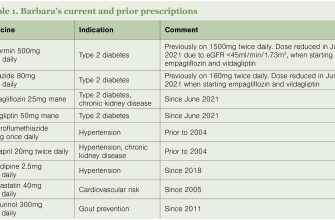
When administering Lisinopril, monitor blood pressure regularly to ensure it remains within the target range. A significant drop in blood pressure can occur, especially after the first dose. Educate patients to check their blood pressure at home and report any persistent readings below 90/60 mmHg.
Assess renal function before initiating therapy. Lisinopril can affect kidney performance, particularly in patients with pre-existing kidney disease. Regularly check serum creatinine and electrolyte levels, particularly potassium, as hyperkalemia can arise. Adjust the dosage if necessary based on lab results.
Advise patients to remain hydrated, particularly after the first dose, to minimize the risk of dizziness or fainting. Eating meals consistently and avoiding excessive potassium-rich foods or supplements will enhance patient safety. Encourage open communication about any side effects, including cough or angioedema, which may necessitate discontinuation of the medication.
Be aware of interactions with other medications, especially diuretics or NSAIDs. A comprehensive medication review supports safe management. Always provide clear instructions and education to foster adherence to the treatment plan.
- Lisinopril Nursing Implications
- Patient Education
- Drug Interactions
- Monitoring Blood Pressure in Patients on Lisinopril
- Assessing for Adverse Effects and Drug Interactions
- Common Adverse Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Patient Education on Lisinopril Administration and Compliance
- Monitoring Blood Pressure
- Adverse Effects Awareness
- Considerations for Special Populations Using Lisinopril
Lisinopril Nursing Implications
Monitor blood pressure regularly to assess the therapeutic response to lisinopril. Target systolic blood pressure typically ranges between 130-140 mmHg for most patients. Be alert for signs of hypotension, particularly in patients who are also on diuretics or have renal impairment.
Assess renal function before and during treatment. Elevated creatinine levels may require dosage adjustments or discontinuation of the medication. Maintain hydration and encourage adequate fluid intake unless contraindicated.
Patient Education
Educate patients about potential side effects, including cough, dizziness, and hyperkalemia. Advise them to report any persistent cough or unusual weakness. Discuss the importance of routine blood tests to monitor potassium levels and kidney function.
Drug Interactions
Review current medication lists for potential interactions, especially with NSAIDs, potassium supplements, and other antihypertensives. Instruct patients to avoid potassium-rich foods and supplements unless specifically advised by their healthcare provider.
Monitoring Blood Pressure in Patients on Lisinopril
Regularly monitor blood pressure in patients taking lisinopril to ensure effective management of hypertension. Measure blood pressure at least once every two weeks during the initial stages of treatment. After achieving stable readings, assessments can shift to monthly intervals.
Utilize an automated blood pressure cuff for accurate readings, as manual measurement may introduce variability. Confirm readings in both arms if discrepancies arise, to identify any potential underlying vascular issues.
Document blood pressure readings meticulously. Track trends over time to identify patterns which may indicate needed adjustments in medication dosage. If systolic blood pressure falls below 90 mmHg or diastolic below 60 mmHg, consider potential adverse effects and consult with a physician.
| Monitoring Frequency | Blood Pressure Readings | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| Weeks 1-2 | Every visit | Adjust based on findings |
| Weeks 3-4 | Every visit | Continue monitoring |
| After 1 month | Monthly | Review treatment efficacy |
| As needed | Monitor if symptoms arise | Consult physician |
Instruct patients to record their daily blood pressure readings at home, if feasible. This can provide valuable insights into blood pressure patterns and help in assessing the effectiveness of lisinopril.
Educate patients about the signs and symptoms of hypotension, such as dizziness or fainting, which may prompt immediate consultation. Encourage them to maintain an appropriate diet and hydration, reducing the risk of significant blood pressure fluctuations.
Assessing for Adverse Effects and Drug Interactions
Monitor patients for signs of hypotension, particularly after the first dose of Lisinopril. Measure blood pressure regularly and educate patients about the importance of reporting dizziness or lightheadedness.
Common Adverse Effects
- Cough: Frequently reported; if persistent, consider switching to another class of antihypertensives.
- Hyperkalemia: Check potassium levels periodically. Advise patients to avoid high-potassium foods and certain supplements.
- Angioedema: Observe for swelling of the face, lips, or throat. If this occurs, immediately discontinue Lisinopril and seek medical attention.
- Renal impairment: Monitor renal function through serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels, especially in patients with pre-existing kidney issues.
Drug Interactions
- Diuretics: Potentiation of hypotensive effects can occur. Adjust diuretic dosage carefully during Lisinopril initiation.
- NSAIDs: May reduce the antihypertensive effect and increase the risk of acute renal failure. Caution is advised when these are co-administered.
- Other Antihypertensives: Monitoring is essential to prevent excessive blood pressure reductions.
- Potassium-Sparing Diuretics: Increased risk of hyperkalemia when used together. Evaluate potassium levels and renal function closely.
Educate patients on the importance of notifying healthcare providers about all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Regular follow-up appointments will help manage potential adverse effects and interactions effectively.
Patient Education on Lisinopril Administration and Compliance
Take Lisinopril exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Consistent daily administration maximizes the medication’s benefits. Aim to take it at the same time each day to establish a routine.
Stay hydrated, especially during hot weather or while exercising, as Lisinopril can affect your blood pressure. Inform your provider if you experience excessive dizziness, as this may indicate low blood pressure.
Monitoring Blood Pressure
Regularly check your blood pressure. Keep a log to record your readings and share it during appointments. This information helps your healthcare team assess how well Lisinopril is managing your condition.
Adverse Effects Awareness
Be aware of potential side effects such as cough, elevated potassium levels, or swelling. Report any unusual symptoms to your provider promptly. Understand that not everyone experiences side effects, but vigilance ensures timely intervention if needed.
Considerations for Special Populations Using Lisinopril
Adjust dosages for elderly patients due to potential renal impairment. Monitor renal function closely, especially during the initiation of therapy, to prevent acute kidney injury. Assess blood pressure regularly to ensure it remains within target levels, as older adults may respond differently to treatment.
For patients with diabetes, evaluate renal function periodically. Lisinopril provides renal protective effects, but dual therapy with diuretics may increase the risk of hypotension and dehydration. Regular monitoring of electrolytes is crucial to prevent hyperkalemia.
In pregnant women, avoid using Lisinopril during pregnancy, particularly in the second and third trimesters, due to the risk of fetal injury. Initiate alternative antihypertensive therapy that is safer for use during pregnancy when necessary.
For patients with a history of angioedema, exercise caution. Assess any previous reactions to ACE inhibitors before prescribing Lisinopril. Discontinue immediately if signs of angioedema occur, as this can be life-threatening.
For patients with heart failure, consider starting at a lower dose and gradually titrating based on tolerance and blood pressure response. Monitor closely for signs of worsening heart failure or hypotension during therapy initiation.